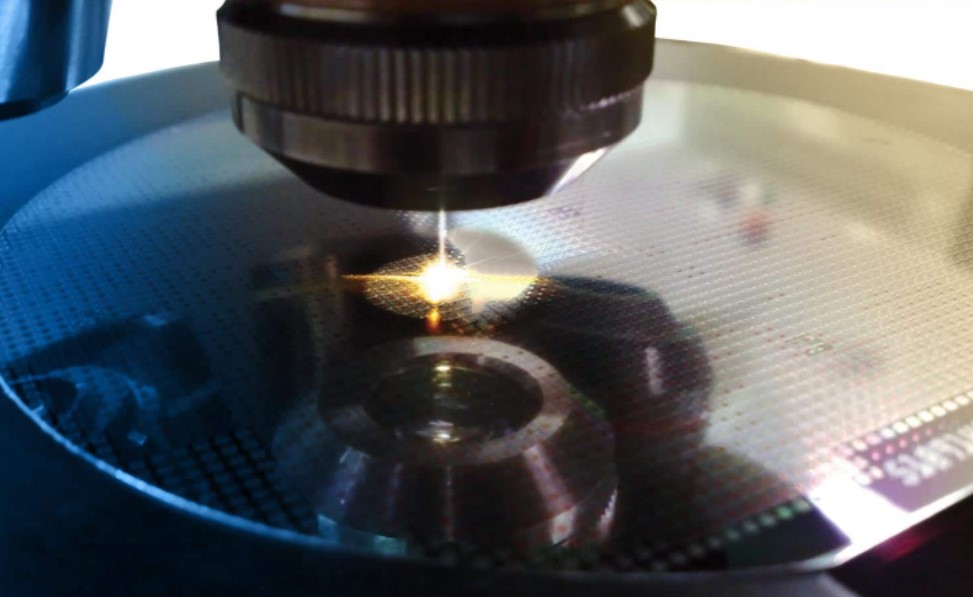
Silicon dicing wafers is a complicated procedure. The first step of the process is to slice the wafer into small pieces. Then, the chips are separated from the wafer by a spinning abrasive disc. The disk rotates at high speeds, and the diamond-studded blades are embedded in an electroplated nickel matrix. The cutting and dicing processes are a crucial part of semiconductor manufacturing.
Wafer Dicing Processes
The silicon wafer cutting process is measured in the number of wafers diced per hour. This measurement is directly related to the blade speed. A higher blade feed rate means higher throughput. To achieve the highest throughput and reduce the damage to the dicing blade, an optimal process selection is needed. The key to successful slicing is to choose a process that meets your requirements and minimizes the risk of chipping.
There are several ways to cut a wafer. Generally, the first step is to cut the wafer. Then, the next step is to shave the edges. For a smooth-fitting package, you can use a roller that presses the dice against the board. A dedicated dicing line between active dice lines allows the cutting of the substrate. The blade’s thickness determines how much material is removed.
The dicing blade is an abrasive, rotating blade. It cuts the wafer and removes debris at the same time. The blade moves along a dedicated line between active areas of the dice, which creates a groove in the material. Once this groove is formed, the wafer will be cut and separated. The dicing process requires precise control over the rate of feeding, and this is why it is crucial to use special monitoring equipment.
The dicing process is measured by the number of wafers diced per hour. The throughput of the dicing process is measured in the number of dice cut per minute. The higher the speed of the blade, the greater the throughput. In general, the dicing technique is characterized by the ability to achieve a high yield while minimizing the risks of damage to the material.
Dicing tape is used to mount wafers. This adhesive tape holds the wafer on a thin metal frame. The tape used to dissect wafers is UV-curable and has different characteristics. In contrast, non-UV dicing tape is used to create larger dies. The dicing process is a crucial part of semiconductor manufacturing and requires careful preparation to achieve the desired results.
The dicing process requires precision and new control capabilities. It can result in a high yield by reducing the number of errors in the cutting process. The resulting wafer dice will be square, rectangular, or triangular. Various variables are monitored during the dicing process. If the process is done correctly, the result is an array of shaped chips. If you’re not satisfied with the results, you may not be able to produce the devices you want.
The dicing process is a complicated process. It involves using a diamond-studded scribe. It cuts the wafer into small pieces, which is called a die. The dicing tape is the only component that comes in contact with the die, and it is made of silicon. It is important to protect the dies and the wafer during the dicing process. In order to protect the dies, the dicing process should be carried out in a clean environment.
The dicing process uses a scribe tool to cut a thin layer of material from a wafer. The scribe tool applies pressure while moving across the wafer. It is then pressed against a surface, which forms a groove on the wafer. It is a fast process and can be performed in a wide range of materials. It is a crucial step in semiconductor manufacturing.
The dicing process is a critical step in the semiconductor manufacturing process. It can result in a high-quality semiconductor. The dicing process can be either continuous or pulsed. One way to make the wafer is by laser ablation. This process involves a pulsed or continuous wave laser. Once the process is complete, the scribe line is then cut to the desired shape. Then, the wafer is broken along the line.